Table of Contents
Toggle1. Xinjiang’s Geographic Location in China
Xinjiang is officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, is in northwest China. It is the largest Chinese province, covering over 1.6 million square kilometers (16% of China’s land).
Borders:
North: Kazakhstan, Russia (Altai region)
West: Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan
Southwest: Afghanistan, Pakistan
Southeast: Tibet Autonomous Region
East: Gansu and Qinghai provinces
2. Proximity to Central Asia: A Crossroads of Cultures
Xinjiang is often called the “Gateway to Central Asia” due to its close ties with countries like Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
Key Distance Examples:
Kazakhstan: The Khorgos border (Xinjiang) is 350 km from Almaty, Kazakhstan’s largest city.
Kyrgyzstan: The Torugart Pass connects Xinjiang to Kyrgyzstan’s Naryn region.
3. Major Geographic Features of Xinjiang
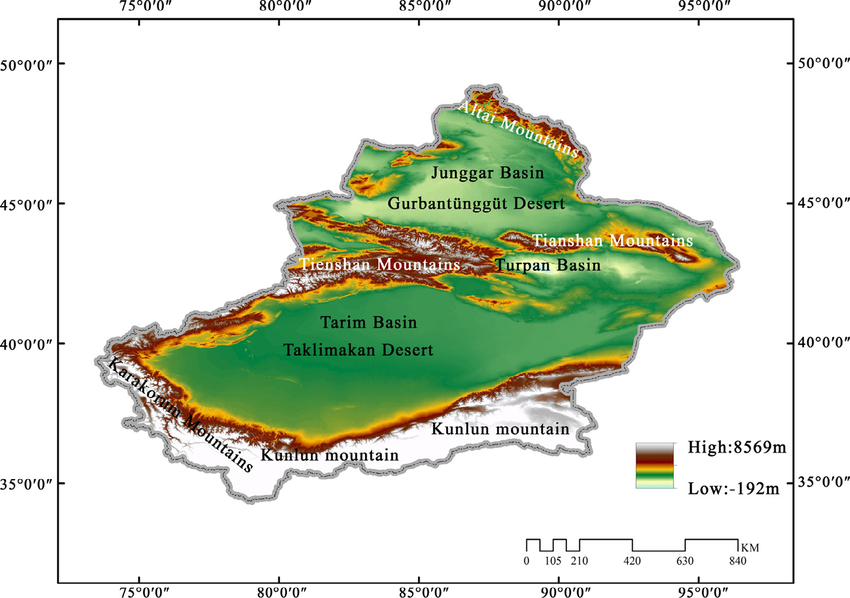
Xinjiang’s landscape is defined by mountains, deserts, and grasslands:
Tian Shan Mountains: Split Xinjiang into Dzungarian Basin (north) and Tarim Basin (south).
Taklamakan Desert: One of the world’s largest deserts, located in the Tarim Basin.
Karakoram Highway: Connects Xinjiang to Pakistan via the Khunjerab Pass.
4. Historical and Cultural Significance
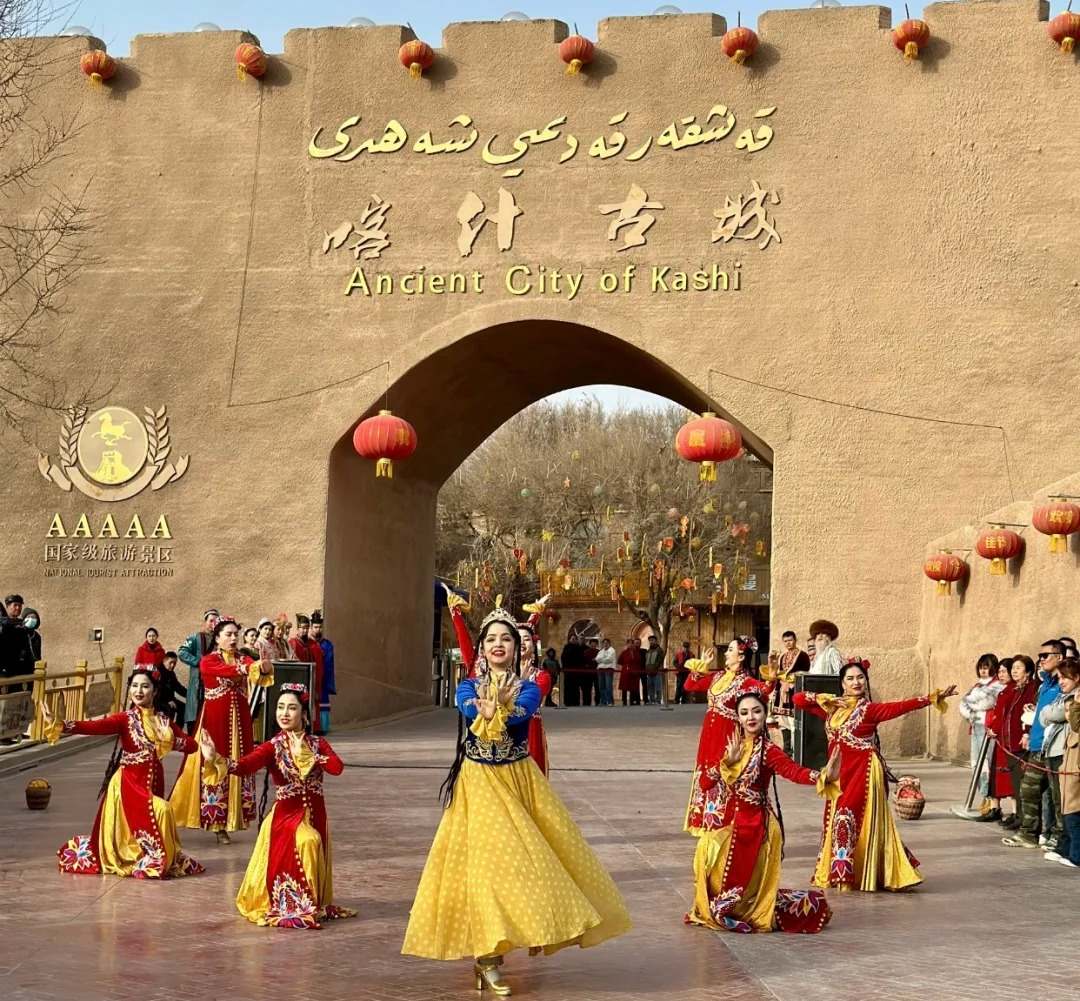
Xinjiang’s location made it a critical part of the ancient Silk Road:
Trade Routes: Linked China to Persia, India, and Europe.
Cultural Mix: Uygur, Kazakh, Han Chinese, and other ethnic groups coexist here.

5. Travel Tips for Visiting Xinjiang
Best Time to Visit Xinjiang: May–October (mild weather).
Permits Required to Visit China: Foreign travelers need permits for border areas.
Cultural Etiquette: Respect local customs, especially in Uygur communities.

Why Xinjiang’s Location Matters
Xinjiang’s position near Central Asia shapes its economy, culture, and geopolitics. It is rich in natural resources (oil, gas) and serves as a hub for China’s Belt and Road Initiative.